When it comes to gardening, one of the most important aspects of growing a successful garden is creating the right environment for your plants. A healthy garden bed is not just about soil but about layering materials that promote proper drainage, nutrient absorption, and the optimal growing conditions for your plants. Whether you’re planting flowers, vegetables, or herbs, building the perfect garden bed can make all the difference in the success of your garden.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through how to create the ideal garden bed step by step, using a variety of materials that will not only enrich the soil but also provide your plants with the nutrients and environment they need to thrive.
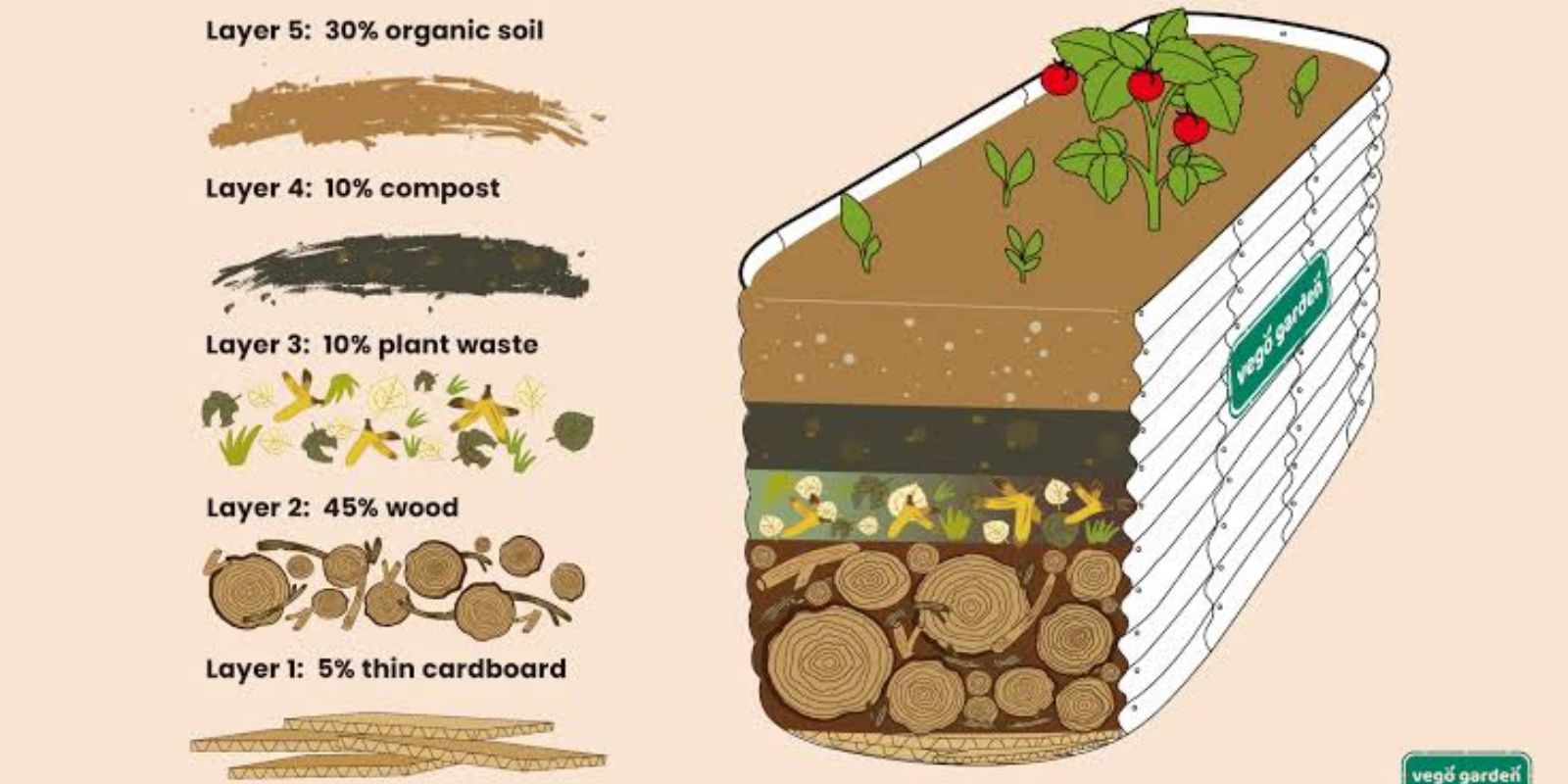
Step 1: Start with a Coarse Layer (Grobe Schicht)
The first step in creating your garden bed is to start with a coarse layer at the bottom. This layer should consist of large, rough materials, such as branches, twigs, or other garden waste like small tree trimmings. The purpose of this coarse layer is twofold: it helps with drainage and elevates the garden bed.
By raising the bed off the ground, you minimize the risk of soil compaction, which can block the flow of air and water to the plant roots. The coarse material also prevents water from pooling in the bed, helping to create an environment where the soil doesn’t become waterlogged. This is particularly important if you live in an area where rainwater tends to accumulate.
Step 2: Add the Green Layer (Grüne Schicht)
Next, you’ll want to add a layer of green plant material. This layer can include things like grass clippings, leaves, or other plant matter that will break down over time. The organic material in this green layer will decompose, providing essential nutrients to the soil as it breaks down.
Green materials are high in nitrogen, which is one of the primary nutrients needed for plant growth. As they decompose, they help to boost the overall fertility of the soil. However, it’s important to make sure the green layer is balanced with the other layers, as too much nitrogen without the right balance of carbon (from brown materials) can lead to issues like excess moisture or a lack of air in the soil.
Step 3: Add an Organic Layer (Organische Schicht)
Once you’ve added the green layer, the next step is to include an organic layer. This layer is made up of compost, decomposed kitchen scraps, or other organic materials such as animal manure. The organic material in this layer provides valuable nutrients that are essential for plant growth, including nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium.
Compost is an excellent addition to any garden bed as it adds beneficial microorganisms to the soil, which help break down organic material and improve soil structure. Additionally, the decomposition process encourages earthworms and other beneficial insects, which help aerate the soil and further enrich it with nutrients. Organic matter also improves the water retention capacity of the soil, which is vital during periods of drought or dry spells.
Step 4: Cover with Fine Soil (Feine Erdschicht)
The next step in creating the perfect garden bed is to add a layer of fine soil. This is the layer in which your plants will grow, so it needs to be rich in nutrients and well-structured to allow the roots to grow deep and strong. You can use a combination of garden soil or potting soil, depending on what your plants require.
Ensure that the soil you choose is rich in organic matter. This will provide your plants with the nutrition they need to grow strong and healthy. You can also enrich the fine soil layer by adding a bit of homemade compost or organic fertilizers. The soil should be loose and well-drained to allow for proper root development, and it should also have a slightly acidic to neutral pH (most plants thrive in a pH of 6-7).
Step 5: Apply a Mulch Layer (Abdeckmaterial)
The final layer of your garden bed is the mulch. Mulch plays an important role in maintaining a healthy garden. It acts as a barrier between the soil and the elements, helping to keep moisture in the soil, suppress weeds, and regulate the temperature. Mulch also helps prevent erosion, which is especially important in areas where heavy rains can wash away topsoil.
There are many types of mulch you can use, including organic materials like straw, wood chips, bark, or grass clippings. You can also use synthetic mulch materials, such as landscape fabric, but organic mulches are preferred because they break down over time, adding to the soil’s organic matter and improving its overall quality.
Mulching is a simple yet highly effective way to protect the soil and improve the growing environment for your plants. Just be sure not to pile the mulch too high against the stems of your plants, as this can cause rot or invite pests.
Why Layering Materials Is Key
So why should you take the time to layer your garden bed rather than simply adding soil and planting directly into it? The answer lies in the different properties of the materials you use. By layering materials in your garden bed, you’re creating an ecosystem that mimics nature’s natural processes.
In nature, leaves fall to the ground, decaying over time and enriching the soil. Plants grow, die, and decompose, returning their nutrients to the earth. By replicating this process in your garden, you’re building a healthy, sustainable environment for your plants.
Furthermore, layering provides better drainage, which is critical for root health. It also helps to regulate the temperature of the soil, keeping it cooler in the summer and warmer in the winter. The organic matter in the soil helps retain moisture, ensuring your plants have access to water when they need it.
Tips for Building a Garden Bed
Here are some additional tips to help ensure the success of your garden bed:
- Consider Your Plants: Different plants have different needs when it comes to soil, water, and sunlight. Be sure to tailor your garden bed to the specific plants you intend to grow. For example, if you’re growing vegetables, you may need to add extra compost or organic fertilizer to meet their nutrient needs.
- Test the Soil: Before you start planting, it’s a good idea to test your soil’s pH and nutrient levels. You can buy a soil test kit or send a sample to a local agricultural extension office for testing. Based on the results, you can amend the soil accordingly.
- Watering: Once your garden bed is built, be sure to water it thoroughly. While you may have added mulch and organic matter to help retain moisture, your plants will still need regular watering to get established. Keep an eye on the moisture level and adjust your watering routine as necessary.
- Regular Maintenance: After planting, continue to maintain your garden bed by removing weeds, replenishing the mulch layer, and adding compost or fertilizer as needed. Regular upkeep ensures that your plants have the best possible environment in which to grow.
Conclusion: The Benefits of Layering for a Thriving Garden
Building the perfect garden bed using layered materials is a simple but highly effective way to ensure your plants thrive. Not only does it improve drainage and provide necessary nutrients, but it also helps regulate temperature and moisture levels for optimal plant growth. By following these steps, you can create a healthy, sustainable environment that will produce beautiful, flourishing plants all year round.
With careful planning and attention to detail, your garden bed will become a source of pride and a testament to your commitment to growing healthy plants. Start layering today and watch your garden thrive!
Ready to build the perfect garden bed? Start layering today and experience the beauty of a thriving garden! 🌱 #GardenTips #HealthySoil #PlantCare #GardenSuccess #SustainableGardening #GardeningHacks #HomeGardening #OrganicGardening