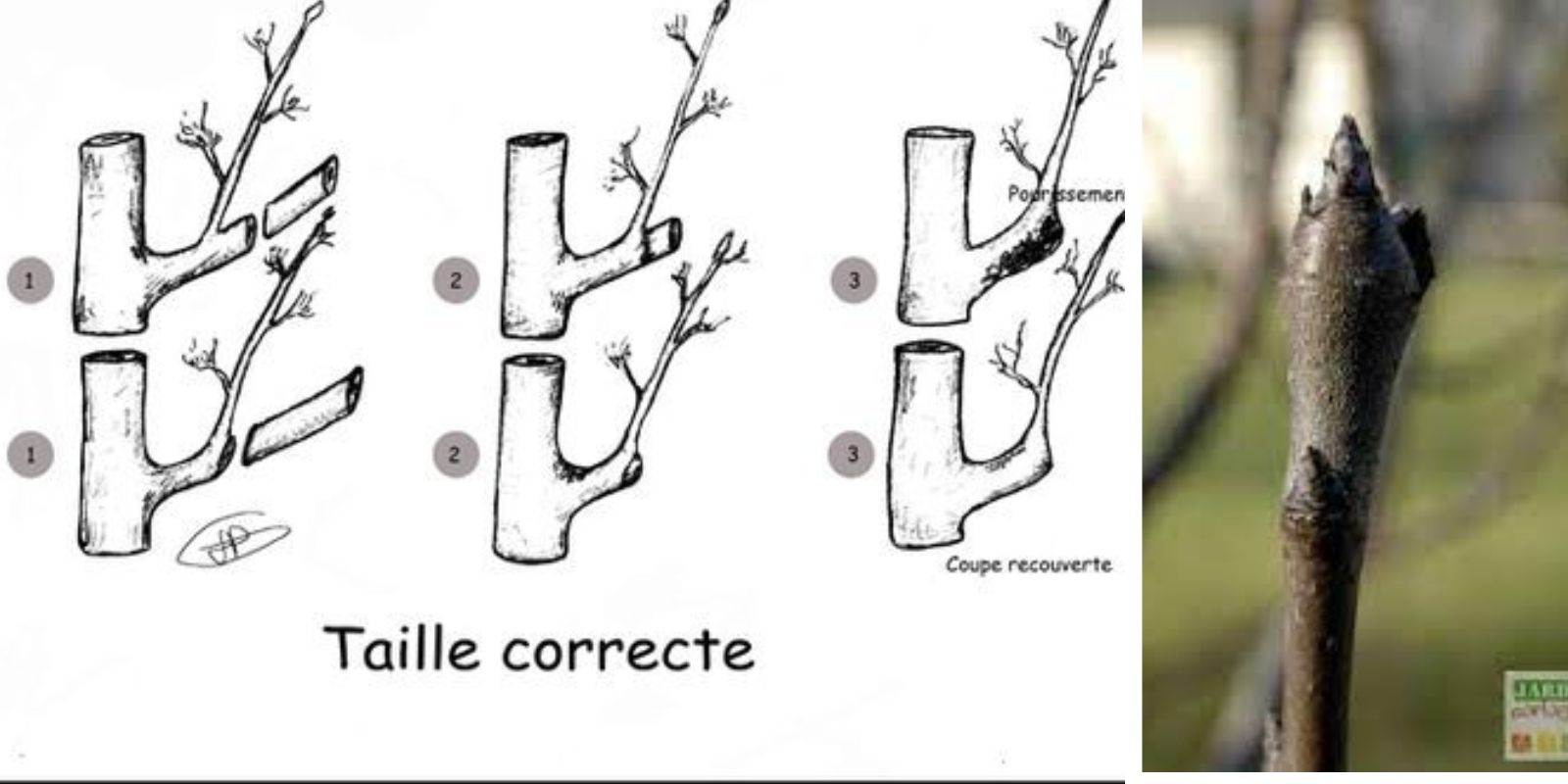
When growing fruit trees, understanding the key growth structures of the tree is essential for ensuring that it thrives and produces a plentiful harvest. Pear trees, with their sprawling branches and delicate fruit, are no exception. Knowing how to identify flower buds, dards, bourses, crown twigs, and lambourdes is crucial for guiding the growth of your tree, making pruning decisions, and ultimately maximizing your yield. This guide will help you recognize these key growth points on your pear tree, equipping you with the knowledge needed to cultivate a healthy, productive pear tree.
Introduction to Pear Tree Growth Structures
A healthy pear tree goes through several stages of growth each season. In order to maximize the tree’s potential, you need to be familiar with the different parts of the tree and how to care for them. The main growth structures that contribute to the tree’s ability to produce fruit include:
- Flower Buds
- Spurs (Dards/Bourses)
- Crown Twigs (Brindilles Couronnées)
- Lambourdes
Each of these structures plays a unique role in the life cycle of the tree, and recognizing them will allow you to make informed decisions on pruning, thinning, and other care practices.
1. Flower Buds: The Foundation of Fruit Production
Flower buds are the first indicator that your pear tree is preparing to bloom and potentially bear fruit. Flower buds are generally larger and rounder than leaf buds, and they will open in the spring to produce the beautiful pear blossoms.
How to Identify Flower Buds:
- Size: Flower buds are larger and rounder compared to leaf buds, which are more slender.
- Color: Flower buds may have a slightly reddish tint when they are still developing.
- Position: Flower buds typically grow on spurs (dards/bourses), which are older parts of the tree.
As the tree matures, it will produce more flower buds, and being able to recognize them will help you ensure that your tree’s growth is directed towards healthy fruit production. Pruning around these buds can be tricky, as you don’t want to remove any of the buds that will yield fruit. In general, flower buds should be left intact during pruning to maximize flowering.
2. Spurs (Dards/Bourses): Vital for Flower and Fruit Production
Spurs, known as dards or bourses in some regions, are short, stubby shoots that grow on older wood and are responsible for bearing flowers and fruit. Spurs are an essential part of pear tree growth because they are the places where new fruits will develop after the tree blooms in the spring.
How to Identify Spurs:
- Appearance: Spurs are short, stubby, and thick compared to other branches. They are often found on older branches and will grow on 1- to 2-year-old wood.
- Position: Spurs generally grow along the main branches or older sections of the tree and can sometimes be found on the trunk.
- Characteristics: They are compact, with no significant elongation like the longer growth shoots. These buds are the parts of the tree that will eventually flower and produce fruit.
Spurs are often considered the “fruiting wood” of the tree, and they should be given particular attention when pruning. Removing too many spurs can significantly reduce the amount of fruit your tree produces, while keeping too many can cause overcrowding and reduce the overall quality of the pears.
3. Crown Twigs (Brindilles Couronnées): Key for Vertical Growth
Crown twigs, also known as brindilles couronnées, are short shoots that grow at the base of the tree, often near the roots or along the trunk. These twigs are important for the tree’s vertical growth, as they help direct the tree’s energy upwards, leading to better structure and form.
How to Identify Crown Twigs:
- Size: Crown twigs are shorter and thicker than regular shoots.
- Position: These twigs typically grow near the base of the tree or along the trunk, helping to push the tree’s growth upwards.
- Growth Pattern: Crown twigs are usually produced in the early years of the tree’s life and help establish a strong foundation for the tree to grow tall.
When it comes to pruning and managing crown twigs, you’ll want to be cautious. Over-pruning crown twigs can result in a stunted tree, while allowing them to grow freely can encourage an uneven structure. For optimal growth, balance the amount of crown twigs with the other growth points on the tree.
4. Lambourdes: Branches That Guide the Growth of Older Pear Trees
Lambourdes are thicker, more mature branches that extend from the main trunk and play a significant role in the tree’s overall structure. These branches, typically seen in older trees, are strong and thick and will eventually bear flowers and fruit after a few years of growth.
How to Identify Lambourdes:
- Size and Strength: Lambourdes are thicker and longer than spurs or crown twigs, often appearing as the main branches of the tree.
- Growth: These branches tend to develop later in the life of the tree, usually after 3 to 4 years, and continue to grow as the tree matures.
- Fruit Production: Lambourdes, being mature branches, will eventually flower and bear fruit after a few years of growth.
Lambourdes are crucial for ensuring that the tree has enough mature wood to bear fruit in future seasons. Pruning these branches should be done carefully, as removing too many can reduce the tree’s capacity to bear fruit in the long run.
Why Recognizing These Growth Structures is Crucial
Recognizing the key growth structures of pear trees helps gardeners make informed decisions about how to care for the tree and manage its growth. Each structure plays an important role in the development of the tree and its ability to produce high-quality fruit.
For example, pruning flower buds, spurs, crown twigs, and lambourdes requires knowledge of the tree’s life cycle and an understanding of which structures are essential for future fruit production. By identifying these growth structures, you’ll be able to:
- Prune Effectively: Knowing which parts of the tree to trim ensures that you don’t remove fruiting wood and that you help guide the tree’s growth.
- Boost Fruit Production: Focusing on the key growth points will help the tree direct energy into healthy fruit-bearing branches.
- Maintain Tree Health: Understanding the role of each structure allows you to avoid over-pruning and ensure that the tree remains healthy and balanced.
Conclusion
Understanding the different growth structures of pear trees is an essential skill for any gardener looking to cultivate a healthy and productive tree. From flower buds to lambourdes, each growth point plays an important role in the development of your tree and its ability to produce delicious, high-quality fruit. By learning to identify these key structures and understanding their functions, you will be well on your way to maintaining a thriving pear tree that produces fruit for years to come.
Start paying attention to these growth points during the growing season, and with the right care, your pear tree will reward you with a bountiful harvest. Whether you are a seasoned gardener or a novice looking to grow your own fruit, mastering the art of pear tree care will give you a deeper connection to your tree and a better understanding of its needs.
Ready to start identifying and caring for your pear tree? Let us know how it goes, and feel free to share your tree care tips with fellow gardeners! 🍐🌱 #PearTreeCare #FruitTreeTips #HealthyHarvest #GardeningSuccess #GrowYourOwnFood #TreeCare #GardenTips #FruitGarden #GardeningCommunity