Aquaponics is a sustainable and innovative method of food production that combines aquaculture (raising fish) and hydroponics (growing plants in water). This closed-loop system creates a symbiotic relationship where fish waste provides nutrients for the plants, and the plants, in turn, help to clean the water for the fish. Not only does aquaponics offer a way to grow fresh produce and fish at home, but it also does so with minimal environmental impact, using less water and space than traditional gardening methods.
In this article, we’ll explore the steps involved in building and maintaining a home aquaponics system. We’ll cover everything from choosing the right location and equipment to selecting the best fish and plants for your system. Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or a beginner, this guide will help you create a thriving aquaponics setup that provides fresh food and a rewarding hobby.
Understanding Aquaponics: The Basics
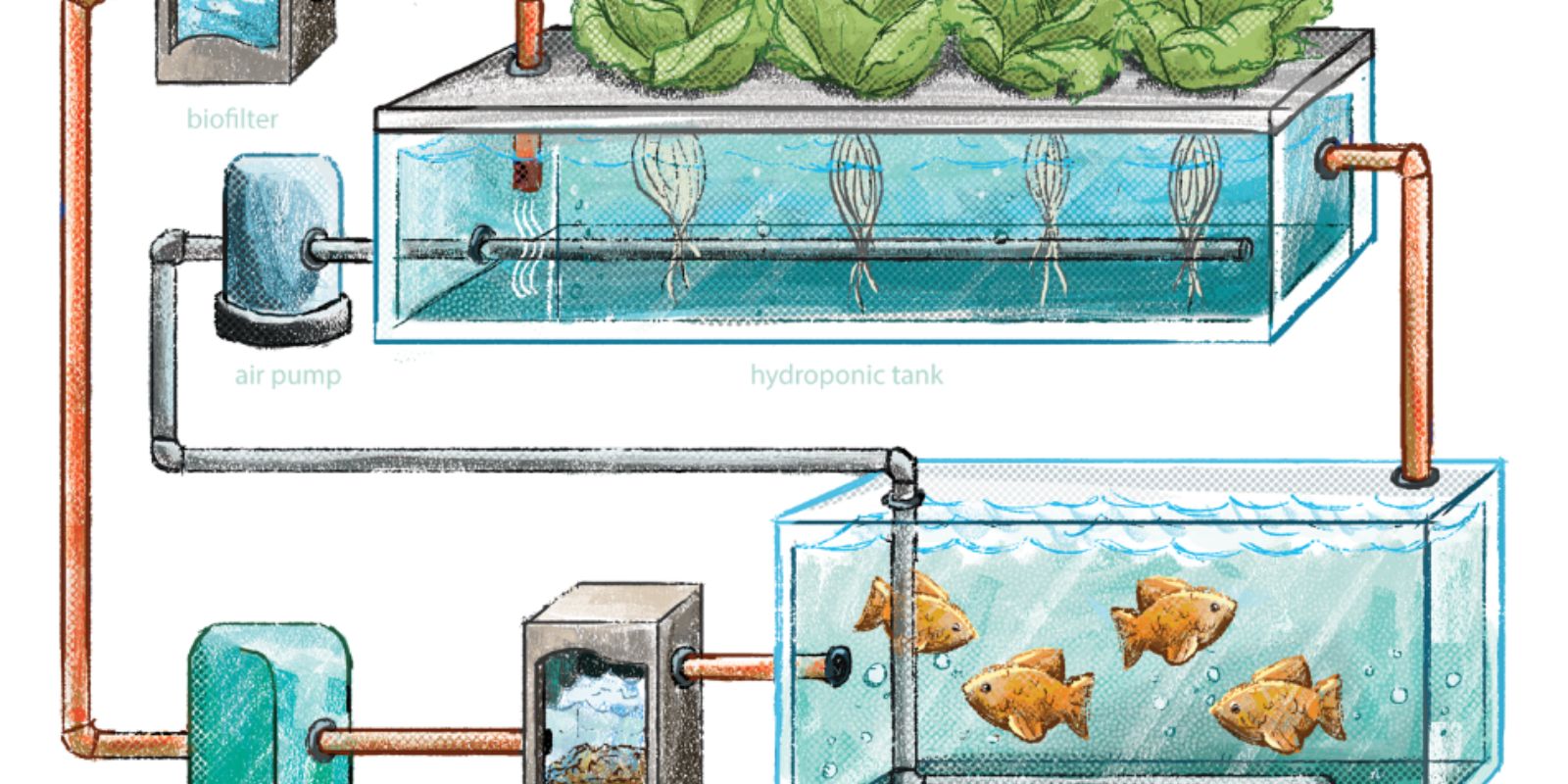
Before diving into the construction and maintenance of your aquaponics system, it’s important to understand how it works. In a basic aquaponics system, fish are raised in a tank, and their waste is converted by beneficial bacteria into nutrients that plants can absorb. The plants, which are grown in a grow bed, filter and clean the water, which is then recirculated back into the fish tank. This continuous cycle creates a balanced ecosystem that requires little external input.
1. The Benefits of Aquaponics
Aquaponics offers numerous benefits, making it an attractive option for home gardeners:
- Sustainable and Eco-Friendly: Aquaponics uses 90% less water than traditional soil-based gardening, making it an excellent choice for areas with limited water resources.
- Space-Efficient: Aquaponics systems can be set up indoors or outdoors, making them suitable for urban environments where space is limited.
- Year-Round Production: With the right setup, you can grow fresh produce and fish year-round, regardless of the climate.
- No Weeding or Soil Pests: Since plants are grown in water, there’s no need to worry about soil pests or weeds.
Step-by-Step Guide to Building Your Home Aquaponics System
1. Choosing the Right Location
The first step in setting up your aquaponics system is selecting the right location. Consider the following factors:
- Light: Most plants require 6-8 hours of sunlight per day. If you’re setting up your system indoors, you’ll need to invest in grow lights that provide the necessary light spectrum for plant growth.
- Temperature: The ideal temperature for most aquaponics systems is between 65°F and 75°F (18°C to 24°C). If you live in a region with extreme temperatures, you may need to insulate your system or use heaters and coolers to maintain a stable environment.
- Space: Determine how much space you have available for your system. Even a small balcony or patio can accommodate a compact setup, while a larger backyard can host a more extensive system.
2. Setting Up the Fish Tank
The fish tank is the heart of your aquaponics system, providing the source of nutrients for your plants. Here’s how to get started:
- Tank Size: The size of your fish tank will depend on the space available and the number of fish you plan to raise. A good rule of thumb is to start with a tank that holds at least 20 gallons (75 liters) of water.
- Material: Fish tanks can be made from various materials, including glass, plastic, or fiberglass. Ensure that the material is food-safe and non-toxic to avoid harming your fish.
- Location: Place the fish tank on a stable, level surface that can support the weight of the water. If you’re setting up the system outdoors, consider using a shaded area to prevent water temperatures from fluctuating too much.
3. Installing the Grow Bed
The grow bed is where your plants will grow, and it’s positioned above or beside the fish tank. Here’s how to set it up:
- Size and Material: The size of the grow bed should be proportional to the fish tank. Most grow beds are made from plastic or other waterproof materials. Ensure that the grow bed has a depth of at least 12 inches (30 cm) to support healthy root growth.
- Growing Media: Fill the grow bed with a growing medium such as gravel, clay pebbles, or coconut coir. This medium will provide support for the plant roots and act as a biofilter, where beneficial bacteria can colonize and convert fish waste into nutrients.
- Positioning: Position the grow bed so that it’s above the fish tank, allowing water to flow from the grow bed back into the tank. This setup helps to aerate the water and create a natural filtration system.
4. Connecting the Water Pump
A water pump is essential for circulating water between the fish tank and the grow bed. Here’s what you need to know:
- Pump Size: The pump should be powerful enough to move the entire volume of the fish tank’s water through the grow bed at least once per hour.
- Plumbing: Use PVC pipes or flexible tubing to connect the pump to the grow bed. Install a drain pipe in the grow bed to allow water to return to the fish tank. You may also want to include a siphon or timer to regulate the flow of water.
- Power Source: Ensure that the pump is connected to a reliable power source. If you’re setting up the system outdoors, consider using a solar-powered pump for an eco-friendly option.
5. Cycling the System
Before adding fish to your system, it’s crucial to cycle the system to establish the necessary beneficial bacteria. This process can take 4-6 weeks and involves the following steps:
- Ammonia Source: Introduce an ammonia source to the system, such as fish food, pure ammonia, or a few hardy fish. Ammonia is a key component in the nitrogen cycle, which is essential for converting fish waste into plant nutrients.
- Monitor Water Parameters: Use a test kit to monitor ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate levels in the water. As the bacteria colonize the grow bed, they will convert ammonia into nitrites and then into nitrates, which are safe for both fish and plants.
- Wait for Stability: Once the ammonia and nitrite levels drop to zero and nitrate levels rise, your system is cycled and ready for fish and plants.
6. Adding Fish and Plants
With your system fully cycled, it’s time to introduce fish and plants:
- Choosing Fish: Select fish species that are hardy and suited to your climate. Common choices for home aquaponics include tilapia, goldfish, catfish, and trout. Ensure that the fish you choose are compatible with the temperature and water conditions of your system.
- Introducing Fish: Acclimate your fish to the water temperature and conditions in the tank before releasing them. Start with a small number of fish and gradually increase the population as the system stabilizes.
- Choosing Plants: Select plants that thrive in the conditions provided by your aquaponics system. Leafy greens (lettuce, spinach, kale), herbs (basil, mint, cilantro), and fruiting plants (tomatoes, peppers, strawberries) are popular choices. Plant seeds or seedlings directly into the grow bed.
Maintaining Your Home Aquaponics System
1. Monitoring Water Quality
Regularly check the water quality to ensure the health of your fish and plants:
- pH Levels: The ideal pH range for most aquaponics systems is between 6.8 and 7.2. Use a pH test kit to monitor levels and adjust as necessary using pH up or down solutions.
- Ammonia, Nitrite, and Nitrate Levels: Keep ammonia and nitrite levels at zero and maintain nitrate levels within a safe range for your fish. Regular testing will help you catch any imbalances before they become problematic.
- Oxygen Levels: Ensure that the water is well-oxygenated, especially if you have a high fish stocking density. You can achieve this by using an air pump or by creating splashes and surface movement with your water pump.
2. Feeding Your Fish
Feed your fish a balanced diet that meets their nutritional needs. Avoid overfeeding, as excess food can decay and lead to poor water quality. Most fish in aquaponics systems require feeding once or twice a day. Monitor their feeding habits and adjust the amount of food based on their appetite and the system’s nutrient needs.
3. Pruning and Harvesting Plants
As your plants grow, you’ll need to prune them regularly to encourage healthy growth and prevent overcrowding in the grow bed. Harvest leafy greens and herbs frequently to promote continuous production. For fruiting plants, harvest the fruits as they ripen to prevent them from taking up too much space or nutrients.
4. Managing Pests and Diseases
While aquaponics systems are less prone to pests and diseases compared to traditional gardens, you may still encounter issues:
- Pests: Use organic methods to control pests, such as introducing beneficial insects, using neem oil, or manually removing pests.
- Diseases: Monitor your plants for signs of disease, such as wilting, discoloration, or mold. Remove any affected plants to prevent the spread of disease.
5. Regular System Checks
Perform regular checks of your entire system to ensure everything is functioning properly:
- Pump and Plumbing: Check the water pump and plumbing for any signs of blockages, leaks, or wear. Clean or replace components as needed.
- Fish Health: Observe your fish for any signs of stress or illness, such as changes in behavior, discoloration, or lesions. Address any issues promptly to maintain a healthy system.
Scaling Up Your Aquaponics System
As you gain experience with your home aquapon
ics system, you may want to expand or scale up. Consider the following:
- Adding More Grow Beds: Increase the size of your grow beds to grow more plants. Ensure that your fish tank and pump can support the additional load.
- Increasing Fish Stocking Density: Add more fish to your system as your grow beds expand. Be mindful of the carrying capacity of your tank and the oxygen levels in the water.
- Exploring Advanced Techniques: Experiment with different types of grow beds, such as deep water culture (DWC) or nutrient film technique (NFT), to diversify your system and increase productivity.
Conclusion: Reaping the Benefits of Your Home Aquaponics System
Building and maintaining a home aquaponics system is a rewarding endeavor that offers fresh produce, healthy fish, and a deeper connection to sustainable living. With careful planning, regular maintenance, and a little patience, you can create a thriving ecosystem that provides food for your family year-round.
So, why not give aquaponics a try? Start small, learn as you go, and soon you’ll be enjoying the fruits (and fish) of your labor. 🌱🐟 #Aquaponics #SustainableLiving #HomeGardening #EcoFriendly #GrowYourOwn #UrbanFarming #GreenThumb