Introduction
Hydroponics, the practice of growing plants in a nutrient-rich water solution without soil, is revolutionizing modern agriculture and home gardening. This method offers numerous benefits, including faster growth, higher yields, and the ability to cultivate plants in confined spaces. Understanding the science behind hydroponics is essential for anyone interested in harnessing its full potential. In this article, we will explore the key scientific principles that make hydroponic gardening effective and successful.
1. Nutrient Delivery
The Role of Nutrients in Hydroponics
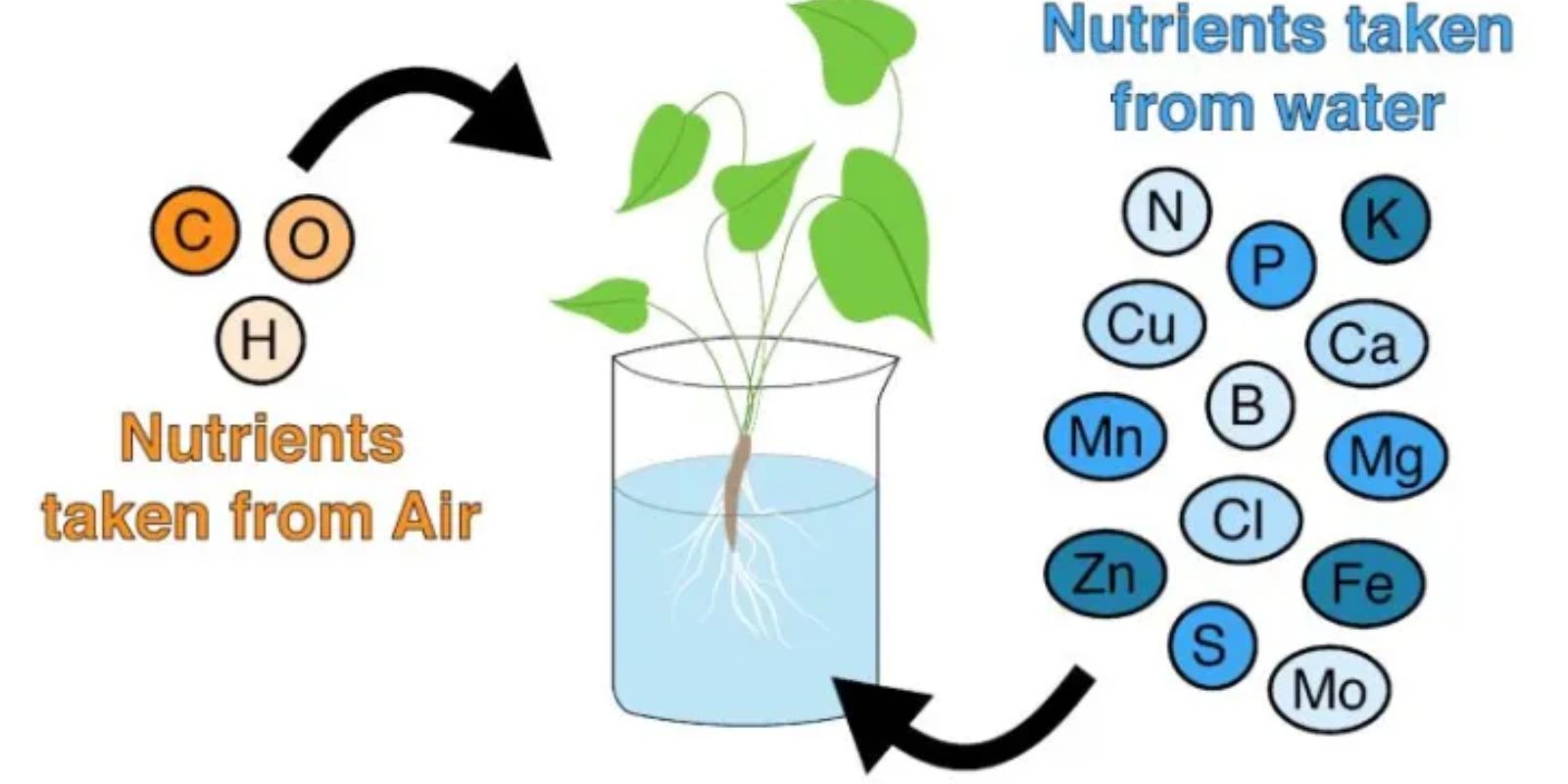
In hydroponics, plants rely on a carefully balanced nutrient solution to obtain the essential minerals and nutrients they need for growth. Unlike traditional soil gardening, where nutrients are absorbed from the soil, hydroponic systems deliver nutrients directly to the plant roots through the water.
Components of Nutrient Solutions
- Macronutrients: These include nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K), which are vital for plant growth and development. They support processes like photosynthesis, root development, and flower and fruit production.
- Micronutrients: Essential for various physiological functions, micronutrients such as calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg), sulfur (S), iron (Fe), manganese (Mn), zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), molybdenum (Mo), and boron (B) are required in smaller amounts but are equally important for plant health.
Nutrient Absorption
Plants absorb nutrients from the water through their roots via a process called osmosis. The nutrient solution must be well-balanced and contain the correct proportions of each nutrient to ensure optimal plant growth and prevent deficiencies.
2. Oxygenation
Importance of Oxygen for Plant Roots
Oxygen is crucial for root health and function. In a hydroponic system, plant roots are submerged in the nutrient solution, which can lead to reduced oxygen availability. Proper oxygenation is essential to prevent root rot and ensure that roots can absorb nutrients effectively.
Methods of Oxygenation
- Air Pumps: Air pumps are used to introduce air into the nutrient solution, creating bubbles that provide oxygen to the roots.
- Air Stones: Attached to the air pump, air stones diffuse air into fine bubbles, enhancing oxygen distribution throughout the solution.
Preventing Root Rot
Maintaining adequate oxygen levels helps prevent root rot and promotes healthy root development. Regularly checking and cleaning air pumps and air stones ensures consistent oxygenation.
3. pH Management
The Role of pH in Nutrient Uptake
pH is a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of the nutrient solution. It plays a critical role in nutrient availability and absorption. Different nutrients are more readily available to plants at specific pH levels.
Optimal pH Range
For most hydroponic systems, the optimal pH range is between 5.5 and 6.5. Within this range, plants can efficiently absorb nutrients and maintain balanced growth. Deviations from this range can lead to nutrient deficiencies or toxicities.
Managing pH Levels
- pH Meters: Use pH meters to regularly check the pH of the nutrient solution.
- pH Adjusters: Adjust the pH using pH up or pH down solutions to maintain the optimal range.
4. Water Quality
The Importance of Pure Water
The quality of water used in hydroponic systems significantly impacts plant health. Contaminants and impurities in tap water can disrupt nutrient absorption and negatively affect plant growth.
Types of Water
- Purified Water: Using purified or distilled water minimizes the risk of contaminants and excess minerals that can interfere with nutrient uptake.
- Regular Monitoring: Regularly test the water for impurities and adjust as needed to maintain a clean and effective growing environment.
5. Light and Temperature
The Role of Light in Photosynthesis
Light is essential for photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy to fuel growth. In hydroponic systems, artificial lighting is often used to provide the necessary light spectrum for plant development.
Types of Lighting
- Fluorescent Lights: Suitable for seedlings and young plants, fluorescent lights are energy-efficient and provide a broad spectrum of light.
- LED Lights: LEDs are energy-efficient and customizable, offering specific light wavelengths to support various stages of plant growth.
Temperature Control
Maintaining the right temperature is crucial for plant health. Most plants thrive in temperatures between 65°F and 75°F (18°C to 24°C). Use fans, heaters, or air conditioners to regulate the temperature in your growing area.
Additional Tips
- Light Duration: Provide plants with the appropriate amount of light based on their growth stage. Typically, plants need 12-16 hours of light per day during the vegetative stage and 8-12 hours during the flowering stage.
- Monitor Temperature: Regularly check and adjust the temperature to avoid stress and ensure optimal growth conditions.
Conclusion
Hydroponic gardening offers a modern and efficient way to grow plants without soil, utilizing a nutrient-rich water solution to provide essential nutrients. Understanding the science behind hydroponics, including nutrient delivery, oxygenation, pH management, water quality, and light and temperature control, is key to successfully cultivating healthy and high-yielding plants.
By mastering these scientific principles, you can optimize your hydroponic garden, overcome common challenges, and enjoy the benefits of soilless cultivation. Embrace the future of gardening with hydroponics and explore the possibilities of growing thriving plants in a controlled and efficient environment. 🌱🔬