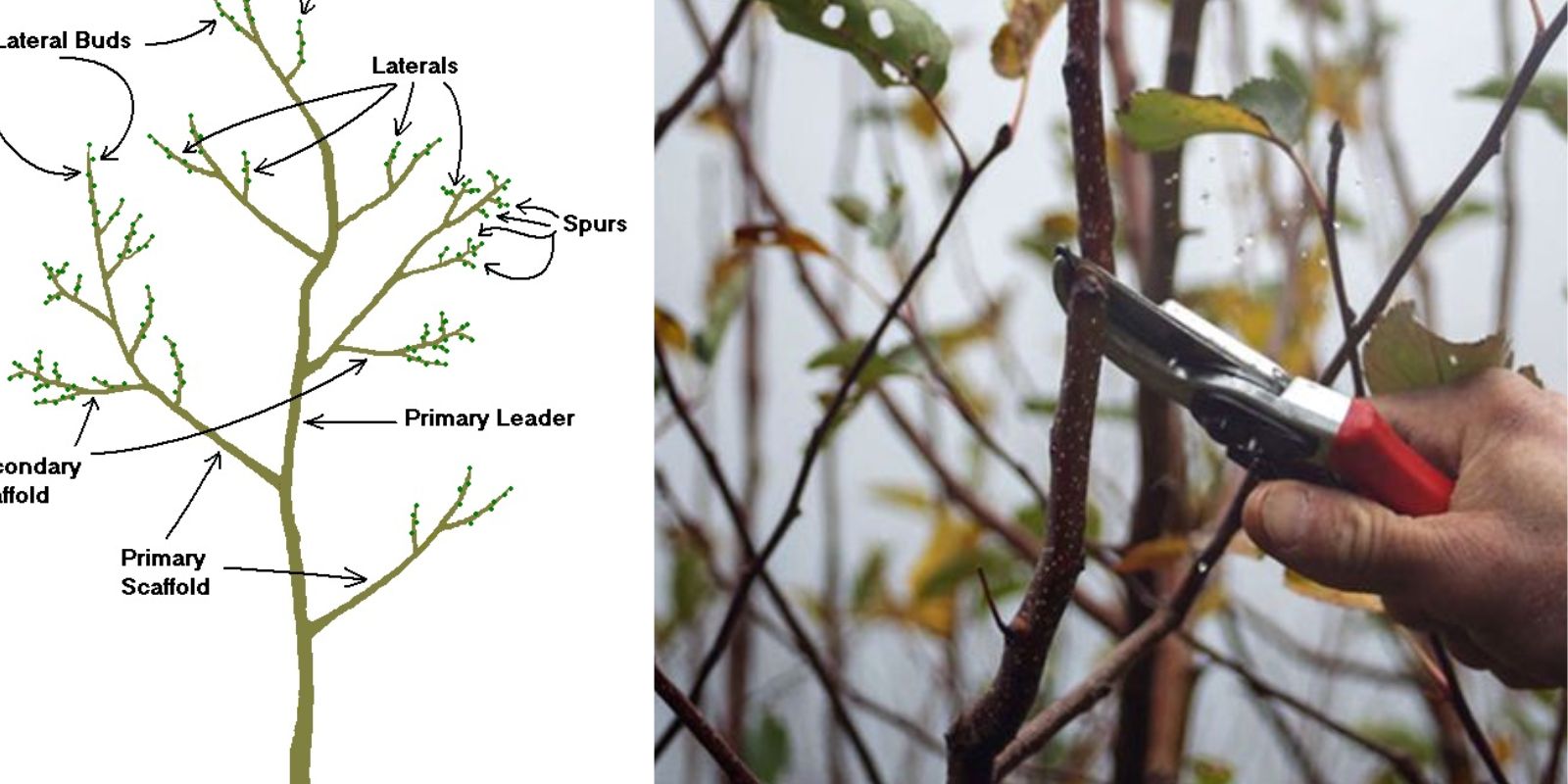
Pruning is a vital horticultural practice that plays a significant role in the health and productivity of fruit and nut trees. Whether you’re managing a small backyard orchard or a larger commercial grove, understanding how to prune effectively can yield delicious rewards in the form of abundant fruits and nuts. This guide will delve into the importance of pruning, the techniques to use, and best practices to ensure your trees thrive.
Understanding the Importance of Pruning
Pruning serves several essential purposes for fruit and nut trees:
- Health Maintenance: Regular pruning helps remove dead or diseased wood, which can harbor pests and diseases. By eliminating these problematic areas, you create a healthier environment for your trees.
- Improved Air Circulation: Pruning enhances air circulation within the canopy, reducing humidity and minimizing the risk of fungal diseases.
- Light Penetration: Proper pruning allows sunlight to reach all parts of the tree, encouraging even growth and fruiting.
- Shape and Structure: Pruning helps maintain a desirable shape, making trees easier to manage and harvest. A well-structured tree is more stable and less prone to breakage.
- Increased Yields: By promoting new growth and ensuring proper spacing, pruning can lead to higher fruit and nut production.
- Longevity: Regular maintenance through pruning can extend the lifespan of your trees, ensuring they remain productive for many years.
When to Prune Your Trees
The timing of your pruning is crucial. The best time to prune most fruit and nut trees is during their dormant season, typically late winter to early spring. This timing allows you to make cuts without interrupting the tree’s growth cycle and reduces stress on the plant. However, some trees, such as summer-bearing varieties, can also be pruned in late summer after they have finished fruiting.
Signs That Your Trees Need Pruning
Before pruning, inspect your trees for several signs that they require maintenance:
- Dead or Diseased Branches: Look for branches that are brittle, discolored, or show signs of decay.
- Crowded Canopy: If branches are crossing or densely packed, it’s time to thin out the growth.
- Weak Growth: Trees that aren’t producing much fruit or show signs of stunted growth may benefit from a thorough pruning.
Tools You’ll Need
Having the right tools is essential for effective and safe pruning. Here’s a list of must-have equipment:
- Pruning Shears: Ideal for small branches (up to ¾ inch in diameter), these should be sharp and comfortable to use.
- Loppers: For larger branches (up to 1.5 inches in diameter), loppers provide extra leverage and cutting power.
- Hand Saw: A pruning saw is necessary for cutting thicker branches (greater than 1.5 inches).
- Safety Gear: Gloves, safety goggles, and possibly ear protection (if using power tools) should be part of your pruning toolkit.
- Disinfectant: Use rubbing alcohol or a bleach solution to sanitize your tools between cuts, especially when working with diseased wood.
Pruning Techniques for Fruit & Nut Trees
Understanding the different pruning techniques is crucial for maintaining healthy trees. Here are some common methods:
1. Thinning Cuts
Thinning cuts involve removing entire branches at their point of origin. This technique is beneficial for:
- Reducing Crowding: Helps maintain proper airflow and light penetration.
- Encouraging New Growth: Stimulates the growth of lateral shoots, leading to better fruit production.
2. Heading Cuts
Heading cuts involve shortening branches to a bud or lateral branch. This technique is helpful for:
- Controlling Size: Keeps trees at a manageable height and shape.
- Promoting Bushier Growth: Encourages new shoots to grow from the remaining buds.
3. Reduction Cuts
Reduction cuts involve removing a branch to a smaller, lateral branch. This method helps:
- Maintain Tree Structure: Keeps trees balanced and prevents heavy branches from becoming a liability.
- Redirect Growth: Guides growth in a desired direction, ensuring even distribution of foliage.
4. Renewal Pruning
For older trees, renewal pruning focuses on removing older, unproductive branches to make way for new growth. This technique helps revitalize the tree and encourages fruiting.
Steps for Pruning Fruit and Nut Trees
Step 1: Assess Your Tree
Begin your pruning process by inspecting your tree carefully. Look for any signs of disease, damage, or overcrowding. Make a plan for which branches to remove based on your observations.
Step 2: Remove Dead or Diseased Wood
Start by cutting away any dead or diseased branches. Make cuts at least 6 inches below any visible signs of disease to ensure you remove all affected areas. This will help protect the tree’s health and prevent the spread of disease.
Step 3: Thin Out the Canopy
Next, focus on thinning the canopy. Remove any crowded or crossing branches, aiming to create an open center for better airflow and light penetration. Aim for a balanced structure where no branch significantly overshadows another.
Step 4: Shape the Tree
After thinning, it’s time to shape the tree. Maintain a natural form while ensuring the tree is well-structured. Avoid removing more than 25% of the tree’s total growth in a single year to prevent stress.
Step 5: Make Clean Cuts
When making cuts, ensure they are clean and at a 45-degree angle. This minimizes the surface area exposed to air and promotes healing. Avoid leaving stubs, as they can lead to decay.
Step 6: Step Back and Evaluate
After completing your pruning, take a step back and evaluate your work. Make sure the tree has a balanced appearance, and no areas are overly crowded.
Step 7: Clean Up
Finally, clean up your pruning debris. Disposing of clippings properly will help prevent the spread of pests and diseases. Consider composting healthy clippings or burning diseased ones to eliminate potential problems.
Best Practices for Pruning
- Know Your Trees: Different fruit and nut trees have varying pruning requirements. Research specific species to understand their needs.
- Use the Right Technique: Match your pruning technique to the tree’s growth stage and condition. Younger trees may need more shaping, while older trees may benefit from thinning.
- Avoid Pruning in Wet Conditions: Pruning when the tree is wet can increase the risk of disease transmission. Choose dry days to perform your pruning tasks.
- Monitor Tree Health: After pruning, continue to monitor the tree for any signs of stress, disease, or nutrient deficiencies. Adjust your care routine accordingly.
- Maintain a Regular Schedule: Pruning should be a regular part of your tree care routine. Aim to prune annually or biannually, depending on the tree’s age and health.
Conclusion
Pruning your fruit and nut trees is an essential practice that enhances their health, structure, and productivity. By understanding the importance of pruning, mastering the right techniques, and following best practices, you can ensure your trees thrive and yield delicious fruits and nuts for years to come.
Whether you’re a novice gardener or an experienced orchardist, investing time in learning how to prune effectively will reward you with a bountiful harvest. Get out there, grab your tools, and start shaping your trees for a fruitful future!
Viral Gardening Hashtags: #FruitTrees #NutTrees #PruningTips #Gardening #HealthyTrees #SustainableGardening #HarvestTime #GreenThumb #HomeGardening #OrganicGardening #TreeCare