Bumblebees are among the most important pollinators in our ecosystems, playing a crucial role in the reproduction of many plants, including numerous crops. Their presence is a sign of a healthy environment, and their decline poses a significant threat to biodiversity and food security. This article will explore the nesting habits of bumblebees, their ecological importance, the threats they face, and how we can help conserve these essential creatures.
The Importance of Bumblebees
Bumblebees belong to the Apidae family and are characterized by their fuzzy bodies and distinct color patterns. Unlike honeybees, bumblebees are social insects that live in colonies, typically consisting of a queen, worker bees, and, later in the season, male bees. They are excellent pollinators due to their unique ability to perform buzz pollination, a technique that allows them to vibrate flowers, releasing more pollen. This method is particularly effective for plants like tomatoes, blueberries, and cranberries, which rely heavily on bumblebee pollination.
In agricultural systems, bumblebees contribute significantly to the pollination of various crops, enhancing fruit and seed production. Their role in wildflower reproduction is equally vital, supporting the overall health of ecosystems and promoting biodiversity.
Understanding Bumblebee Nests
Bumblebees typically nest in small colonies, often consisting of 50 to 400 individuals. They prefer to establish nests in undisturbed areas with suitable materials for building their homes. Here are some key characteristics of bumblebee nesting habits:
Nesting Locations
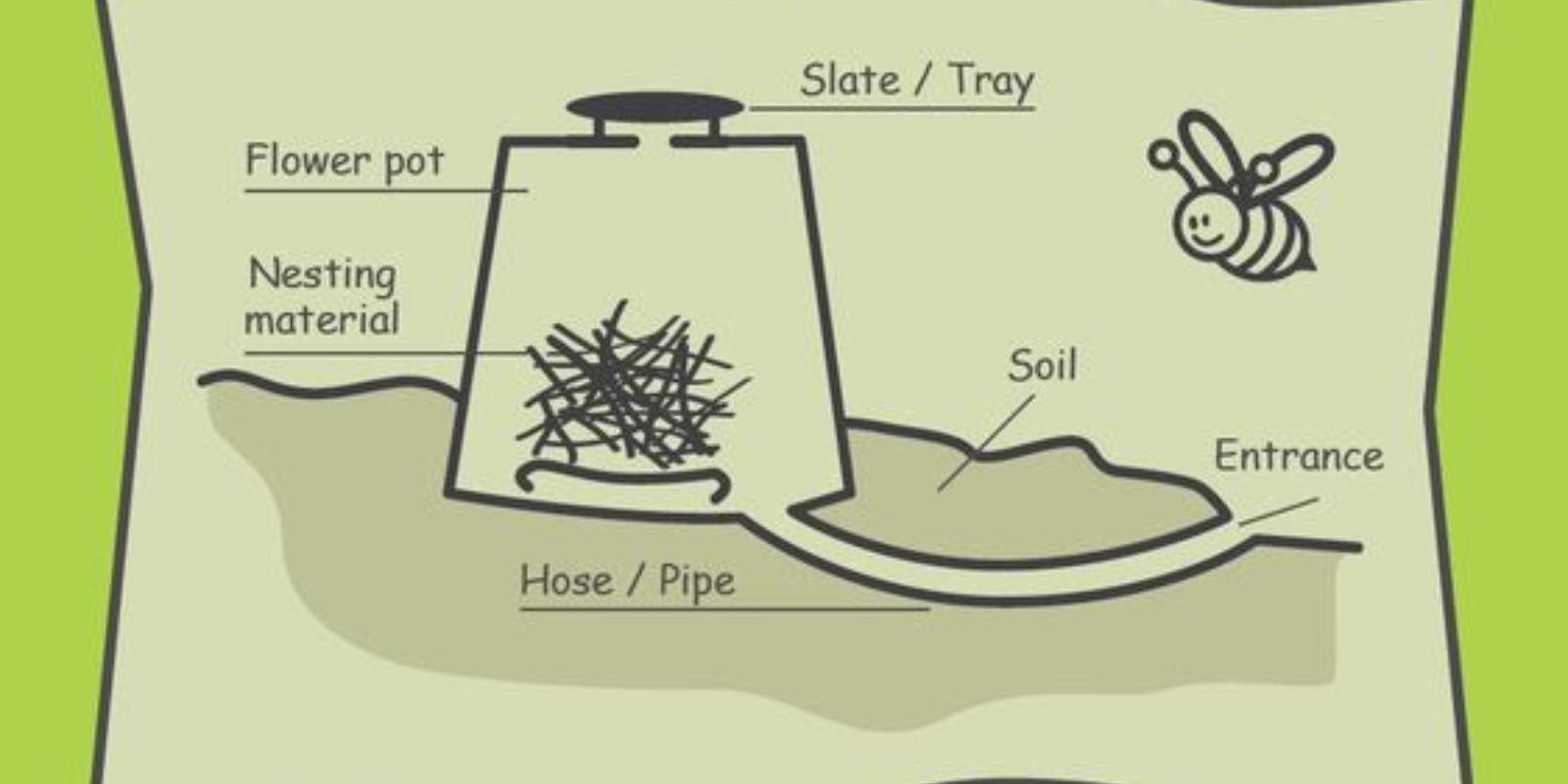
- Underground: Many bumblebee species prefer nesting underground in abandoned rodent burrows or in grass tussocks. They seek sheltered areas that offer protection from predators and harsh weather conditions.
- Above Ground: Some bumblebee species also nest in above-ground locations, such as in dense grass, shrubs, or even in man-made structures like birdhouses and garden sheds.
- Compost Heaps: Compost piles provide a warm, insulated environment that is often favored by bumblebees. The organic matter offers both nesting material and warmth, making it an attractive site.
Nest Construction
Bumblebees construct their nests using various materials, including:
- Plant Fibers: They gather dried grass, moss, and plant fibers to create a soft, warm environment for their young.
- Wax: Bumblebees produce wax from special glands on their bodies, which they use to build combs for rearing their young.
- Pollen and Nectar: Bumblebee nests typically contain a mix of pollen and nectar, which serves as food for the developing larvae.
Life Cycle in the Nest
Bumblebee colonies operate on a seasonal cycle:
- Spring: In early spring, the queen emerges from hibernation and searches for a suitable nesting site. She collects materials and lays her first batch of eggs.
- Summer: As the eggs hatch and the larvae develop into workers, the colony grows. The workers take over foraging and caring for the young, allowing the queen to focus on laying more eggs.
- Fall: In late summer and fall, the colony produces new queens and males. After mating, the new queens find a safe place to hibernate, while the rest of the colony dies off as temperatures drop.
- Winter: The cycle begins anew in spring when the new queens emerge from hibernation.
Threats to Bumblebee Populations
Despite their critical role in ecosystems, bumblebee populations have been declining due to various factors:
Habitat Loss
Urbanization, agricultural expansion, and deforestation have led to significant habitat loss for bumblebees. As natural spaces shrink, so do nesting sites and food sources, making it challenging for bumblebees to survive.
Pesticide Use
The widespread use of pesticides, particularly neonicotinoids, has detrimental effects on bumblebee populations. These chemicals can impair navigation, foraging behavior, and reproductive success, leading to colony decline.
Climate Change
Climate change poses a significant threat to bumblebees as it alters their habitats and affects flowering times. Mismatches between the timing of flower blooms and bumblebee activity can lead to food scarcity, further endangering their populations.
Disease and Parasites
Bumblebees are also susceptible to diseases and parasites, such as the Nosema fungus and the Varroa mite. These pathogens can spread quickly within colonies, leading to declines in population health.
How to Support Bumblebee Nests
As gardeners and nature enthusiasts, we can play a vital role in supporting bumblebee populations. Here are some effective strategies:
1. Create Suitable Nesting Sites
To help bumblebees thrive, provide suitable nesting habitats in your garden:
- Leave Undisturbed Areas: Designate areas in your garden where grass can grow tall and wild. These undisturbed spots can serve as ideal nesting locations.
- Install Bee Hotels: Consider installing bee hotels or nesting boxes that provide shelter for solitary bees and may also attract bumblebees.
2. Plant Pollinator-Friendly Flowers
Cultivating a diverse range of flowering plants is crucial for attracting bumblebees and providing them with food sources. Choose plants that bloom at different times throughout the growing season to ensure a continuous supply of nectar and pollen. Some excellent choices include:
- Lavender
- Sunflowers
- Bee Balm
- Coneflowers
- Foxglove
- Clover
3. Avoid Pesticides
Minimize or eliminate the use of chemical pesticides in your garden. Instead, opt for organic pest control methods and natural alternatives to keep your plants healthy without harming pollinators.
4. Educate and Advocate
Spread awareness about the importance of bumblebees and their conservation among friends, family, and local communities. Consider organizing workshops or community events focused on pollinator-friendly gardening practices.
5. Participate in Citizen Science
Get involved in citizen science projects aimed at monitoring bumblebee populations. Many organizations offer programs that allow individuals to report bumblebee sightings, contributing valuable data for conservation efforts.
6. Support Local Conservation Initiatives
Contribute to local conservation organizations focused on protecting bumblebee habitats and promoting sustainable agricultural practices. Donations or volunteer work can significantly impact bumblebee conservation efforts.
Conclusion
Bumblebees are vital allies in our gardens and ecosystems, contributing to biodiversity and food security. By understanding their nesting habits, recognizing the threats they face, and taking proactive steps to support their populations, we can create a more sustainable environment for these essential pollinators.
Through simple actions like providing suitable nesting sites, planting diverse flowers, and avoiding harmful pesticides, we can all make a difference in bumblebee conservation. Together, we can help ensure that these incredible creatures continue to thrive and pollinate the plants that nourish our world.
Join the movement to protect bumblebees and create a thriving ecosystem! 🐝🌼 #BumblebeeConservation #PollinatorFriendly #SaveTheBees #GardeningForBees #EcoFriendlyGardening